

NAD Iontophoresis Patch: Advanced Transdermal Delivery System for Enhanced Absorption
NAD+ therapy has become increasingly popular in wellness and longevity circles. Many seek convenient alternatives to traditional IV administration.
Iontophoresis patches represent a revolutionary approach to NAD+ supplementation. These NAD+ patches can boost NAD+ levels by up to 5 times. They also eliminate the need for invasive procedures, making them accessible for home use.
The technology behind these patches uses a process called iontophoresis. This process facilitates enhanced absorption of NAD+ through the dermal layers.
Unlike oral supplements that face digestive breakdown, iontophoresis patches provide direct delivery to the bloodstream with high bioavailability. Users typically wear these medical-grade patches for approximately four hours weekly. This makes them significantly more convenient than time-consuming IV sessions.
Beyond convenience, these non-invasive patches offer pain-free administration while delivering therapeutic doses of NAD+. The benefits extend to supporting metabolism, genomic stability, and DNA repair—all crucial aspects of cellular health and longevity.
Understanding NAD Iontophoresis
NAD+ iontophoresis represents a cutting-edge approach to delivering this vital coenzyme directly into the bloodstream through the skin. This technology combines biological science with electrical engineering to bypass digestive breakdown and maximize cellular absorption.
The Role of NAD in the Body
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) serves as a critical coenzyme in cellular metabolism. It facilitates hundreds of enzymatic reactions, particularly those involved in converting food into energy.
NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, contributing to various aspects of the aging process. This reduction impacts cellular energy production, DNA repair mechanisms, and overall cellular health.
The molecule plays a crucial role in activating sirtuins, proteins that regulate cellular health and longevity. These "longevity genes" depend on adequate NAD+ to function properly.
Supplementing NAD+ can potentially support:
- Improved energy production
- Enhanced cellular repair
- Better cognitive function
- Regulated circadian rhythms
Every NAD+ molecule has a specific "half-life" in the body, determining how long it remains active before breaking down. Traditional oral supplements face significant degradation during digestion.
Principles of Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis technology uses mild electrical charges to transport NAD+ molecules through the skin barrier directly into the bloodstream. This process creates a charge gradient that effectively pushes the NAD+ molecules across the skin.
The system typically consists of two electrodes that generate this electrical current. When applied, the patch initiates a charge that propels the medication through the skin in a completely pain-free manner.
Unlike injections or IVs, transdermal iontophoresis patches release NAD+ slowly over approximately 12 hours. This extended release significantly increases therapeutic efficacy compared to methods with rapid clearance.
The process maintains the structural integrity of NAD+ molecules, preserving their bioactivity. By bypassing the digestive system, a higher percentage of active NAD+ reaches target cells.
Studies show this delivery method can increase NAD+ bioavailability by up to 90% compared to oral supplements, which typically achieve only 2-3% bioavailability.
Design and Components of the NAD Iontophoresis Patch
The NAD iontophoresis patch combines advanced technology with strategic materials to enable effective transdermal delivery of NAD+ molecules. The innovative design creates a complete system for non-invasive administration while eliminating the need for lengthy clinical visits.
Anatomy of the Patch
The NAD iontophoresis patch features a multi-layered structure that works together to deliver NAD+ molecules through the skin barrier. At its core lies a specialized drug reservoir containing the NAD+ solution, positioned directly against the skin surface for optimal contact and delivery.
The patch includes a power source component that generates the mild electrical current essential for iontophoresis. This current helps propel the charged NAD+ molecules through the skin's layers with precision.
Integrated battery systems power the iontophoresis mechanism, enabling consistent delivery over extended periods—typically up to 12 hours. This extended release timeframe allows for maximum therapeutic benefit compared to other administration methods.
The design features electrodes strategically positioned to create the electrical field necessary for driving the molecules through the skin barrier efficiently.
Materials and Technology
The patch utilizes iontophoresis technology that employs mild electrical currents to enhance the transdermal delivery of NAD+. This approach overcomes the skin's natural barrier function through gentle electrical stimulation rather than physical penetration.
Biocompatible materials ensure the patch remains comfortable during extended wear while minimizing potential skin irritation. These materials are selected specifically for their conductivity and hypoallergenic properties.
The NAD+ solution within the reservoir is specially formulated for stability and optimal molecular charge to facilitate effective electrical transport through skin tissues. This formulation ensures the NAD+ remains bioactive throughout the delivery process.
The patch design includes moisture management features to maintain proper electrical conductivity without causing skin maceration during extended wear periods. This balance is crucial for maintaining both comfort and effectiveness throughout the treatment duration.
Clinical Applications and Efficacy
NAD+ iontophoresis patches demonstrate significant therapeutic potential across multiple medical domains. Clinical studies indicate measurable benefits for skin conditions, pain management protocols, and addressing cellular aging processes.
Dermatological Uses
NAD+ delivered through iontophoresis shows remarkable effectiveness for skin rejuvenation and repair. The technology promotes faster cellular repair in skin tissues, helping reduce visible signs of aging and improving overall skin health. This targeted approach ensures NAD+ reaches specific dermatological problem areas with precision.
Clinical applications include treatment of photodamaged skin, where NAD+ supports DNA repair mechanisms compromised by UV exposure. The patches have shown promise in addressing hyperpigmentation by regulating melanin production through NAD+-dependent pathways.
For inflammatory skin conditions like rosacea and eczema, NAD+ iontophoresis provides anti-inflammatory benefits without systemic side effects. The non-invasive nature of these patches makes them particularly suitable for sensitive skin patients who cannot tolerate more aggressive treatments.
Chronic Pain Management
The non-invasive drug delivery capability of NAD+ iontophoresis patches offers significant advantages for chronic pain management. Clinical trials demonstrate effectiveness in reducing inflammatory pain conditions through NAD+'s role in cellular energy production and inflammation modulation.
These patches provide sustained release of NAD+ directly to affected tissues, bypassing gastrointestinal absorption issues common with oral medications. This approach may reduce reliance on conventional analgesics with their associated side effects.
For neuropathic pain conditions, NAD+ supports nerve cell function and repair by enhancing mitochondrial energy production. Patients with diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia have reported improved pain scores in preliminary studies.
The technology enables precise dosing and controlled delivery, making it suitable for long-term pain management strategies without developing tolerance issues common with many pain medications.
Age-Related Conditions
NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, contributing to various age-related pathologies. Iontophoresis patches offer targeted delivery to counteract this decline, showing promising results for age-related metabolic disorders and cognitive function.
Clinical applications include supporting mitochondrial function in tissues affected by age-related degeneration. This approach has shown potential benefits for muscle strength and endurance in elderly patients through improved cellular energy production.
For cognitive health, NAD+ delivery via iontophoresis may support neuronal energy metabolism and reduce oxidative stress. Early clinical observations suggest possible benefits for memory and cognitive processing speed in older adults.
The patches also show promise for metabolic health parameters, including glucose regulation and lipid metabolism, which commonly deteriorate with advancing age.
Usage Guidelines and Safety
Proper application and awareness of potential side effects are essential for safe and effective use of NAD+ iontophoresis patches. Following manufacturer instructions precisely ensures optimal delivery of NAD+ through the skin barrier.
Application Instructions
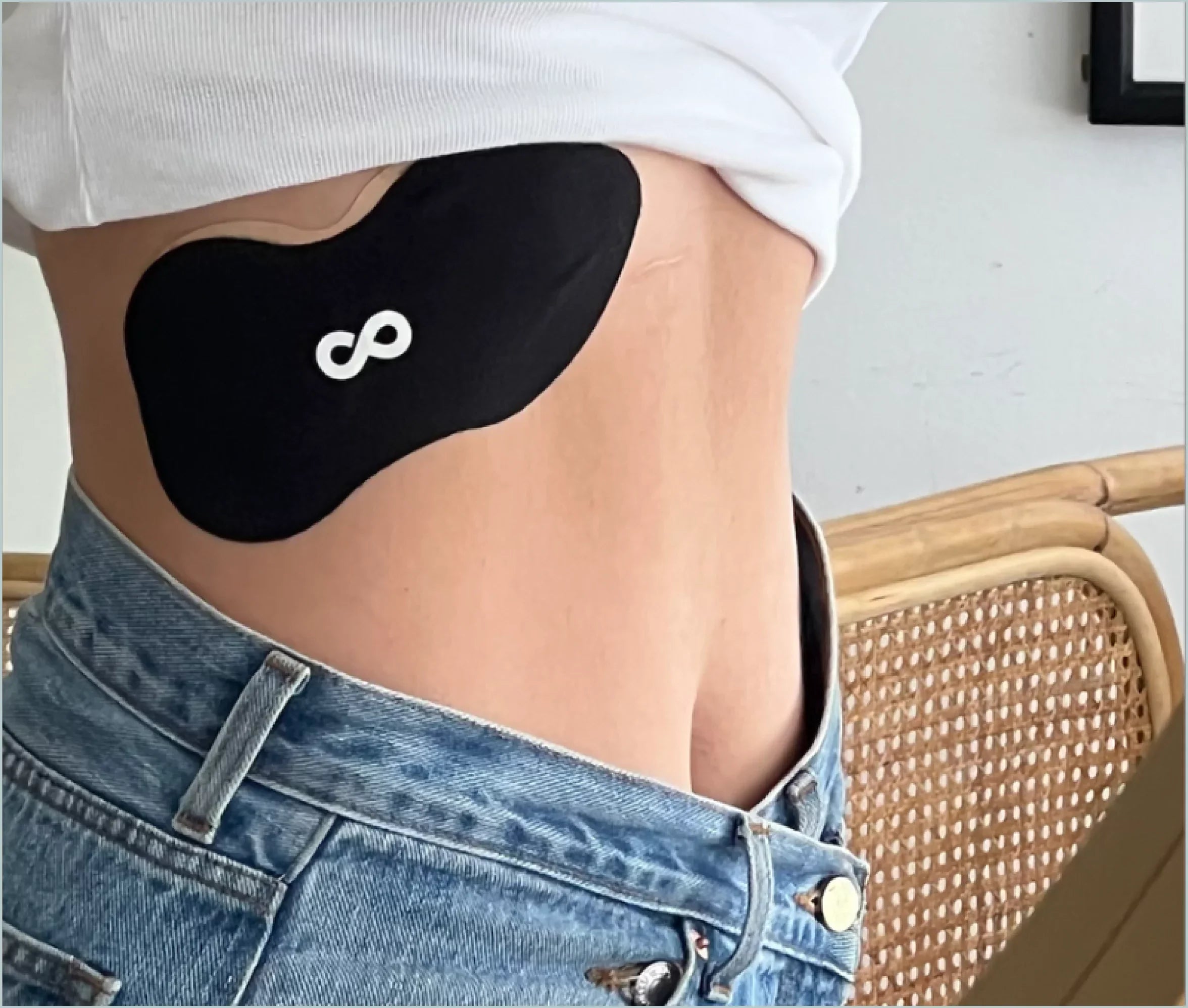
NAD+ iontophoresis patches should be applied to clean, dry skin without hair, oils, or lotions that could interfere with adhesion. Most patches are designed for placement on areas with good blood flow such as the inner wrist, upper arm, or abdomen.
Before application, thoroughly wash and dry the selected area. Remove the protective backing and firmly press the patch onto the skin, ensuring complete contact around all edges. The iontophoresis mechanism utilizes positive and negative charges to pulse NAD+ through the skin.
Typical wear time ranges from 4-12 hours depending on the specific product. Do not exceed the recommended duration as this won't increase effectiveness but may increase irritation risk.
Replace patches according to your prescribed schedule. Most NAD+ patches are designed for single patient use and require proper disposal after removal.
Potential Side Effects and Contraindications
Most users experience minimal side effects with NAD+ iontophoresis patches. The most common reaction is mild skin irritation at the application site. This irritation typically resolves quickly after patch removal.
Common side effects may include:
- Temporary redness or itching
- Mild tingling sensation
- Skin irritation at patch site
Individuals with certain conditions should consult healthcare providers before use:
- Those with sensitive skin or dermatological conditions
- Pregnant or nursing women
- Individuals with electronic implanted devices (pacemakers)
- Patients with impaired skin integrity
NAD+ patches should not be applied to broken skin, rashes, or irritated areas. Discontinue use and consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent irritation, severe redness, or unusual reactions. The non-invasive nature of iontophoresis makes it generally safer than injectable alternatives, but proper precautions remain important.